What is GAF in Child Psychology?
This question is often asked by students and even parents who want to understand how psychologists measure mental health in children. The Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF) is a tool that helps experts evaluate how well a child is doing in daily life—socially, emotionally, and academically. In this article, we’ll break it down step by step so you can understand it easily.
What is GAF in Child Psychology?
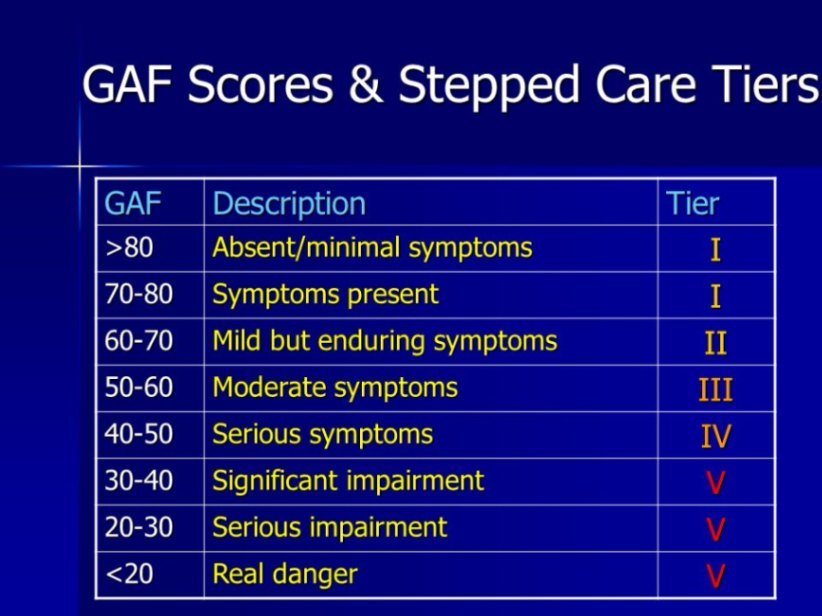
GAF stands for Global Assessment of Functioning. It is a scoring system used by psychologists to understand how well a child is functioning in their everyday life. The score usually ranges from 0 to 100, where:
- 100 means excellent functioning (no problems at all).
- 50 means serious difficulties (trouble at school, home, or with friends).
- 0 means very severe issues (unable to function normally).
This system was widely used to check mental health in both children and adults. Although some modern tools have replaced it, GAF is still very important to learn because it gives a simple way to measure how mental health affects daily life.
Why was GAF Created?
The idea was to make a standard method so that doctors, teachers, and parents could understand how a child is doing without using complicated medical terms. It made communication about mental health easier and clearer.
Why is the GAF Score Important in Child Psychology?
The GAF score plays a big role in child psychology because it helps in understanding the level of support a child needs.
Helps Identify Mental Health Issues
If a child has a low score, it shows that they may have trouble with school performance, friendships, or emotional control. This helps teachers and parents to step in early and provide help.
Guides Treatment Plans
Psychologists use the score to decide what kind of therapy, counseling, or special support might be needed. For example, a child with a score of 60 may need different support compared to a child with a score of 30.
Easy to Track Progress
Over time, psychologists can use GAF to track if a child is improving, staying the same, or getting worse. This makes it easier to adjust the treatment plan as needed.
How is GAF Used to Understand Children’s Mental Health?
GAF in child psychology is not just about giving a number. It’s about understanding the child’s whole life experience.
Daily Life Functioning
A psychologist looks at whether the child can manage daily routines such as going to school, finishing homework, playing with friends, and following rules at home.
Emotional Health
They check if the child feels happy, anxious, sad, or angry most of the time. If emotions are too strong or hard to control, it affects the GAF score.
Social Behavior
Can the child make friends, keep friendships, and behave well in groups? Social life is an important part of mental health.
Academic Performance
Since school is a big part of a child’s life, grades, class participation, and focus are also considered while scoring.
The Role of GAF in Child Psychology Assessments
Psychologists don’t only look at symptoms—they use GAF to see the bigger picture of a child’s life.
Helps in Diagnosis
If a child is showing signs of anxiety, depression, or behavioral problems, GAF is used as part of the diagnostic process. It gives a quick snapshot of how serious the problem is.
Useful for Teachers and Parents
When parents or teachers hear a GAF score, they can understand the child’s struggles clearly. Instead of just saying “the child is struggling,” a number gives a measure of how much support is needed.
Supports Long-Term Planning
If a child has ongoing difficulties, the GAF score can be used to decide on long-term strategies, like special education support or regular counseling.
Examples of GAF Scores in Child Psychology
Sometimes it’s easier to understand GAF through examples.
Example 1: High Score (80–100)
A 12-year-old who does well in school, has friends, and enjoys hobbies may get a score above 80. This shows that the child is functioning well with no major mental health issues.
Example 2: Moderate Score (50–70)
A child who struggles with anxiety, sometimes avoids school, and has trouble focusing in class may score around 60. This means they need support but are still able to manage daily life.
Example 3: Low Score (Below 40)
A child who cannot attend school regularly, avoids friends, and has emotional breakdowns often may score below 40. This shows serious problems that need professional treatment and constant support.
How Do Psychologists Measure a Child’s GAF Score?
Psychologists use the GAF system to observe and rate different areas of a child’s life. The goal is not only to give a score but also to understand how well the child is functioning.
- Interviews: The psychologist often talks with the child and parents to learn about emotions, school life, and daily behavior.
- Questionnaires: Sometimes, teachers or parents fill out forms to describe how the child behaves in class or at home.
- Observation: Psychologists watch how the child acts in real situations, such as during play or learning activities.
- Behavior Records: School reports and past medical history are also used.
By combining all this information, they assign a score between 0 and 100. This gives a clear picture of the child’s overall mental and emotional health.
Benefits of Using GAF for Children’s Mental Health
Using GAF in child psychology has several advantages that make it a helpful tool for professionals, parents, and even students.
Easy to Understand
Instead of complex medical words, the score is simple—just a number. Parents and teachers can quickly understand what the child is going through.
Helps in Communication
A GAF score allows psychologists to explain mental health in a way that everyone can understand. This improves teamwork between parents, teachers, and health professionals.
Guides the Next Steps
If the score is low, it signals that the child needs extra care. If it’s high, it means the child is doing well. This makes it easier to decide on therapy, counseling, or extra school support.
Tracks Progress Over Time
Since the GAF score can change, psychologists can use it to check if the child’s condition is improving with treatment or getting worse.
Limitations of GAF in Child Psychology
Even though GAF is useful, it has some drawbacks.
Too Simple for Complex Problems
Children may have multiple issues at the same time, such as learning difficulties, emotional struggles, and social challenges. A single score might not capture all of these.
Depends on the Psychologist’s View
Two different psychologists might give slightly different scores to the same child because it is based on personal judgment.
Not Always Updated
Some experts say that GAF is an older system, and newer methods are more detailed. Still, GAF is taught to students because it explains mental health in an easy way.
Alternatives to GAF in Child Psychology
Since GAF has some limits, other tools are also used in modern psychology. These alternatives provide a more complete picture of a child’s mental health.
- Children’s Global Assessment Scale (CGAS): Similar to GAF but made especially for children.
- DSM-5 Assessment Measures: A newer method that looks at symptoms in detail.
- Behavior Rating Scales: Used by teachers and parents to report daily behavior.
- Emotional and Social Checklists: Focus on how the child feels and interacts with others.
While these tools may be more detailed, GAF remains popular in teaching because it is easy to explain and understand.
Final Thoughts: Why Students Should Know About GAF in Child Psychology
Understanding GAF in child psychology is important for students who want to learn about mental health in a simple way. Let’s sum it up in key points:
- It gives a score from 0 to 100 to show how well a child is functioning.
- The score covers school, social life, emotions, and family behavior.
- It helps parents, teachers, and doctors work together to support the child.
- Even though it has limitations, it is still valuable for learning and teaching.
By understanding how GAF works, students can better comprehend how mental health is assessed and why support systems are crucial.
Conclusion
GAF in child psychology is one of the easiest ways to understand a child’s overall functioning. It provides a simple score that explains how well a child is doing in daily life, from schoolwork to friendships and emotions. While it is not a perfect system, it is still an important tool for students to learn because it introduces the basic idea of mental health assessment in a way that is easy to understand. Parents and teachers benefit from it because they can see where a child needs extra support.
Although newer systems exist, GAF remains valuable for teaching students about the connection between mental health and daily life. Learning about GAF helps us realize that mental health is just as important as physical health, and it shows us how psychologists work to make sure children grow in a healthy and balanced way